Maryland: Aligning Implementation of the National Diabetes Prevention Program Across Payers and Health Systems
December 2019 | 6|18 Initiative State Spotlight
Through the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) 6|18 Initiative, Maryland’s Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Control, Office of Population Health Improvement, and Medicaid program partnered to decrease diabetes incidence among Marylanders by aligning National Diabetes Prevention Program (National DPP) implementation with its statewide all-payer activities.
Prior to its participation in CDC’s 6|18 Initiative, Maryland made significant strides in its diabetes prevention efforts. Maryland was one of two states that participated in a Medicaid demonstration project from July 2016 through January 2019. Funded by CDC’s Division of Diabetes Translation and led by the National Association of Chronic Disease Directors (NACDD), the demonstration supported implementation of the National DPP lifestyle change program for Medicaid beneficiaries at high risk for type 2 diabetes through managed care organizations (MCOs).
MARYLAND KEY FACTS
- State population: 6.04 million
- Medicaid population: 1.4 million
- Medicaid enrollees in managed care: 85 percent
- Prevalence of diagnosed diabetes among adults: 9.6 percent
- Dollars spent on diabetes per capita: $861
Maryland’s 6|18 Accomplishments
- Maryland Medicaid‘s §1115 waiver amendment was approved by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), authorizing the state to offer the National DPP lifestyle change program to eligible managed care participants, effective September 1, 2019.
- The Maryland Department of Health is providing support and technical assistance to its nine Medicaid MCOs during the roll-out of this coverage, including the four MCOs that participated in the original demonstration, as well as five that are new to the effort.
- Maryland supports its CDC-recognized lifestyle change program provider organizations, by: (1) championing that these sites become Medicaid-enrolled providers; (2) helping them connect with MCOs; and (3) hosting business-planning workshops.
6|18 Project Activities
Maryland’s goals within CDC’s 6|18 Initiative were to: (1) promote implementation alignment of the National DPP across payers and health systems; and (2) enhance provider referrals to the National DPP lifestyle change program. Specific activities undertaken by the Maryland team, with support from NACDD and Leavitt Partners (a health care consulting firm), include:
 1. Increase Provider Awareness, Education, and Training to Enhance National DPP Lifestyle Change Program Referrals
1. Increase Provider Awareness, Education, and Training to Enhance National DPP Lifestyle Change Program Referrals
The Maryland team enhanced referrals by expanding electronic referral approaches and developing a National DPP education campaign for primary care providers. The state’s diabetes prevention efforts emphasized provider practice transformation, including, for example, incorporating National DPP lifestyle change program referral processes into provider practices to increase program participation and creating feedback loops between referring providers and CDC-recognized organizations delivering the lifestyle change program to facilitate follow-up as necessary. As part of these efforts, Maryland created Shared Learnings for Integrating the National DPP into Hospitals and Health Systems, which includes information about capacity building, recruitment and referrals, provider engagement, National DPP implementation and data sharing, and payer reimbursement.
Maryland also developed a National DPP Process Flow map, at the request of its state-designated health information exchange, the Chesapeake Regional Information System for our Patients (CRISP), and in collaboration with NACDD and Leavitt Partners. The process flow map outlines the procedure for referring and enrolling individuals into the National DPP lifestyle change program and delivering the program to those individuals, and can be used to help inform where to leverage CRISP’s support. Through its participation in 6|18, Maryland also engaged additional key provider organization stakeholders, including the Maryland Hospital Association and the Maryland Primary Care Program.
 2. Align Diabetes Prevention Goals with Population Health Objectives under Maryland’s All-Payer Model
2. Align Diabetes Prevention Goals with Population Health Objectives under Maryland’s All-Payer Model
Maryland sought to align its 6|18 payer and health system engagement strategy with its ongoing diabetes prevention efforts. As part of Maryland’s All-Payer Model and subsequent Total Cost of Care Model, the state developed a Population Health Measurement Framework to track improvement on targeted population health indicators and align statewide engagement to improve population health. Maryland selected diabetes prevention as one of the first focus areas for the framework and developed a statewide, all-payer population health target to hold health systems and payers accountable for diabetes prevention. Under 6|18, Maryland sought to align its National DPP-related measures to support the statewide Population Health Measurement Framework. In addition, Maryland regularly monitors National DPP coverage (reimbursement) among payers — Medicare, Medicaid and commercial — across the state.
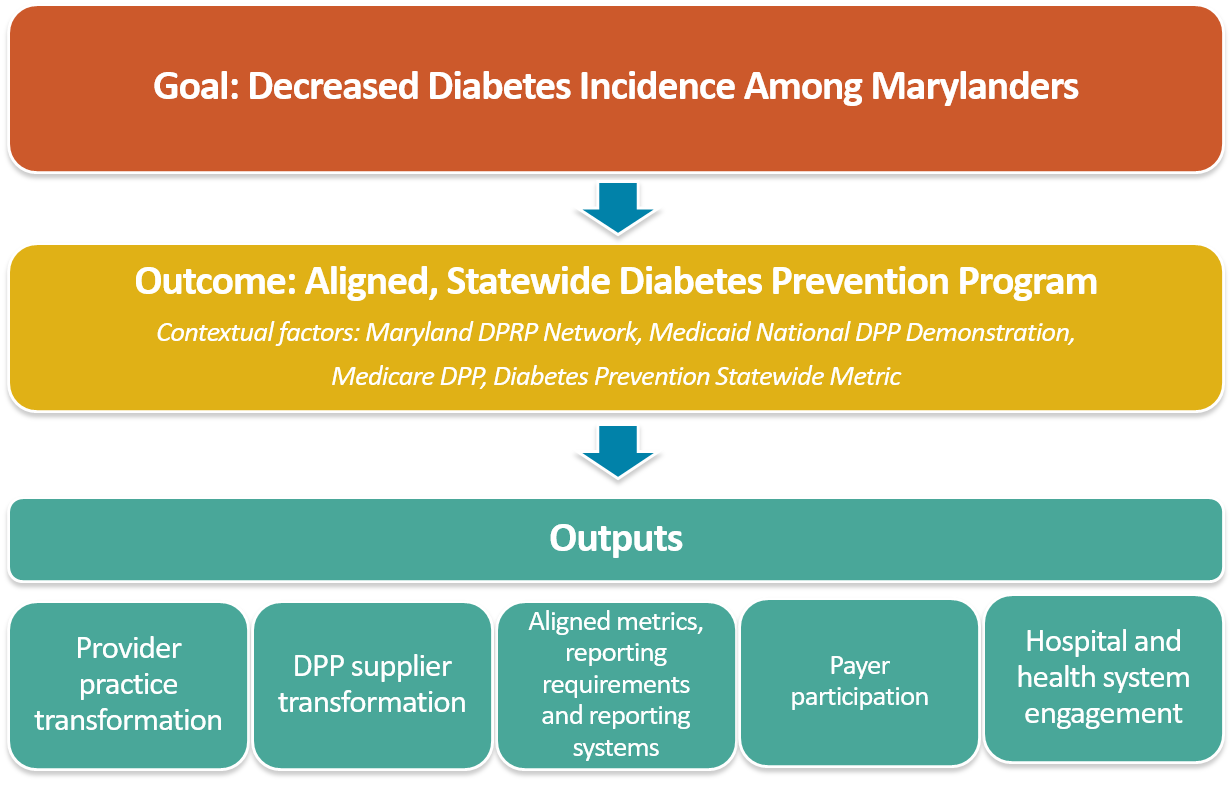
Maryland HealthChoice DPP Expansion Conceptual Framework
To support both its 6|18 activities and the state’s broader diabetes demonstration, Maryland developed the following conceptual framework to illustrate its vision of a statewide expansion of the National DPP program (see diagram below). To support successful statewide expansion, the following elements (outputs, or primary drivers) will be necessary: (1) established provider practice transformation that includes provider referral processes and feedback loops; (2) a sufficient and sophisticated network of National DPP suppliers (CDC-recognized organizations); (3) aligned metrics, reporting requirements, and systems; (4) payer participation; and (5) hospital and health system engagement.
State Spotlights: Medicaid-Public Health Collaboration in CDC’s 6|18 Initiative
This profile is part of a series, developed by the Center for Health Care Strategies and made possible by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, that showcases how state Medicaid and public health departments are using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) 6|18 Initiative to accelerate the adoption of evidence-based prevention efforts focused on improving health outcomes and controlling health care costs. The CDC’s 6|18 Initiative links proven prevention activities to health coverage and delivery with a focus on six high-burden, high-cost health conditions — tobacco use, high blood pressure, inappropriate antibiotic use, asthma, unintended pregnancies, and diabetes.